Computer-assisted surgery is the use of computer technology to perform and plan a surgical procedure. Optical surgical navigation is considered, the passage of computer surgery as a traditional basic element leading to tactile control, stereoscopic vision, manual dexterity and complete visual control of the surgical field.
As technological progress has steadily improved the health sector, the world of medical image acquisition and processing has also undergone a similar revolution. Most surgeons are familiar with the concepts of multilayer, high-definition spiral CT, high-resolution MRI and functional imaging such as PET, as well as the ability to process the entire flow of data so that the end user can perform three-dimensional (3D) reconstructions or image fusion; as a result, an important proportion of our surgical planning processes is already based on medical imaging.
Surgical Navigation Systems
These navigation systems help the execution and organization within the surgical field, allowing to guide the instruments that are connected to screens by sensors with imaging methods such as CT or MRI. These navigation systems are among the hospital equipment that has been increasingly used, making the intervention not only easier, but also safer, in view of the fact that they serve as a kind of physician’s assistant.
Navigation operating systems are an integral part of computer-assisted surgery (CAS), which represents a concept that supports surgical procedures with base in digital imaging technology.
In this context, navigation systems provide an opportunity for surgeons to develop preoperative planning and precise navigation of instruments during the surgical procedure. Similarly, platforms in 3D models, used virtual navigation technology corresponding to the anatomy of the patient and in which surgical instruments used by the surgeon, are followed by an optical location device, so that their virtual image can be displaced within the model.
Mixed or enhanced reality also refers to the use of visual pre-operative information directly on the treatment area of the patient, and through potentiation, allows the surgeon to locate internal structures as a guide to the phases of the operation, in which the surgeon must use special lenses or a stereoscopic helmet where the images fusion takes place. Thus, the surgeon harmonizes the appropriate reconstruction of the patient, in which the patient’s movements are monitored by an optical or electromagnetic tracking system. The computer not only matches real-time vision with 3D reconstructions based on pre-operative images, but also simplifies image-based assessments.
Benefits in the Use of Navigation Systems
Optical surgical navigation systems are methods designed to assist and accurately locate anatomical structures in open or percutaneous procedures. These systems provide optical tracking capabilities as well as integration with external devices such as microscopes and ultrasound. Through the use of these optical navigation systems, the following benefits are presented:
- It ensures processes that are safer to generate data in any process within the operating room
- Allow remote access for live broadcasts from the operating room to auditoriums or even other hospitals where other specialists can view procedures to guide or support decisions made by the medical team during the procedure.
- It allows greater safety in operations because this technology provides surgeons with smaller instruments.
- Infection control, avoiding that the surgeon is contaminated with other elements outside the surgical field, having better management on the visualization of different cuts of anatomical structures that are projected as supportive images in the operating rooms.
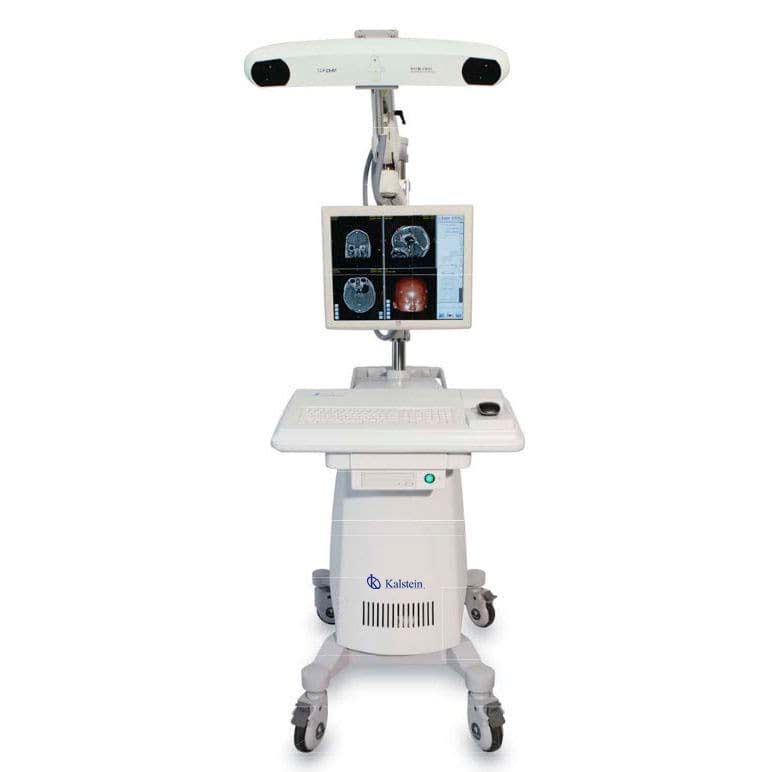
Kalstein Optical Surgical Navigation System
With the use of new technologies in surgical navigation systems, Kalstein offers innovative equipment as standard YR which is widely used for surgical visualization, planning and navigation in which minimizes medical risks, also has tomographic images in DICOM and captured with CT / C-arm / MRI / fMRI are applicable in the surgical navigation system YR02143, which guides active or passive markers that provide accuracy with advanced optical tracking systems. The method of 3D simulation and modeling of anatomical structures in material (such as skin, skull, brain tissue, or target lesion) can be easily defined for surgical convenience. Using navigation systems, it provides operators with intelligent software that will help calibrate and compensate for unexpected changes in anatomic structure and brain change induced by removal of the area of intracranial injury.
At Kalstein, we have the best advice you can enjoy and the range of products that meet your requirements, for this, enjoy our catalog HERE We are manufacturers and we offer you the best prices so that your purchase is the right one.
I invite you to check out HERE