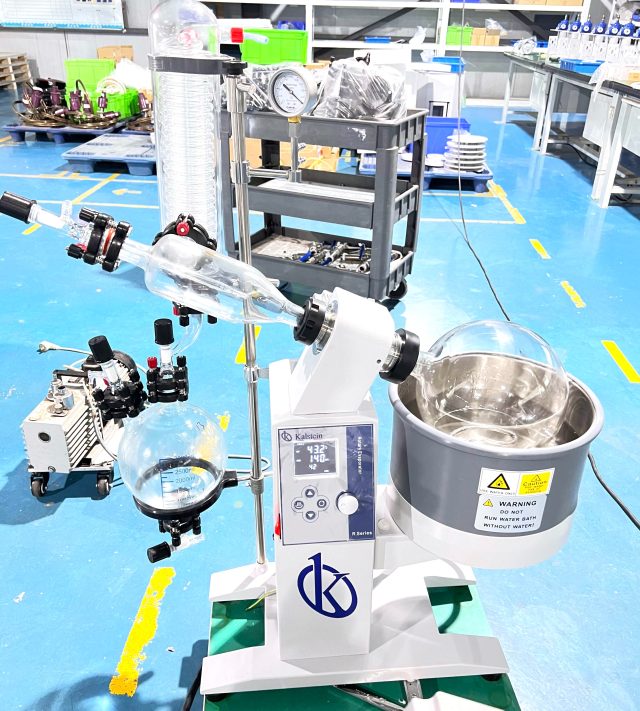
A rotary evaporator is laboratory equipment designed to facilitate the evaporation of liquids at high temperatures. It is an essential tool in the biology laboratory, where it is used to concentrate samples and perform other tasks related to research. The rotary evaporator consists of an evaporation tank, a heating unit, a condensing unit and a vacuum pump. All these elements are connected to each other by a series of pipes and hoses.
The rotary evaporator is a very versatile tool and can be used to carry out a wide variety of tasks in the laboratory. For example, it can be used to distil liquids, concentrate samples, perform chemical reactions, and extract organic compounds from solid samples. It is also often used in the qualitative and quantitative analysis of compounds. In qualitative analysis, it is used to determine whether a sample contains a particular compound. In quantitative analysis, it is used to determine the amount of a compound present in a sample.
Kalstein-branded rotary evaporators are a vital piece of equipment in many laboratories, and can be used for a variety of purposes. By understanding how they work and how to use them, you can ensure that your lab experiments are successful.
Rotary Evaporator Operation
The operation is based on the pressure difference between the laboratory atmosphere and the interior of the evaporation tank. Evaporation is done by heating to a temperature higher than that of the liquid to be evaporated. This creates a vacuum, which in turn causes the liquid to evaporate at a lower temperature. The condensing unit is used to cool the steam produced during the evaporation process, allowing the liquid to condense and be collected in the evaporation vat.
This tool is very useful for the biology laboratory, as it allows to perform a wide variety of research tasks in a more efficient way.
To use the equipment, the sample is placed in the rotating flask and the hot plate is lit. The vacuum pump operates and begins to remove air from the system. As air is removed, the pressure inside the flask decreases and the boiling point of the solvent decreases. This causes the solvent to evaporate from the sample and be collected into the condenser. Once the desired amount of solvent has been extracted, the vacuum pump is turned off and the system is cooled. The sample may then be removed from the flask and the collected solvent reused.
General Characteristics
They consist of a few key pieces, a rotating flask into which the sample is placed, a condenser that cools the vapors and a vacuum pump that removes air from the system. The vacuum pump is connected to the rotary evaporator through a vacuum line, and the entire system is placed on a hot plate. It is an adapted version of the distillation equipment used in the processing of chemical and petrochemical products. The aim of distillation is to separate liquid mixtures by evaporation, according to their boiling points. It also consists of a boiler that is heated by a water bath, a hood that is placed on the boiler and that is equipped with a hose that takes the liquid to distil, and a condenser. This process is often used to purify or concentrate samples, and can also be used to recover solvents that have been used in previous steps of a reaction.
Kalstein Rotary Evaporator
Today, equipment must be easy to maintain high quality standards that are reliable and efficient. That is why Kalstein with its technological contributions during the manufacture of the multiple medical and laboratory equipment, meet the demands of customers. We have the Rotary Evaporators belonging to the YR series, it has patented design structure, the angle of inclination of the evaporation flask is adjustable. The quick lock button on the rotation axis makes it easy to install or remove and Rotational speed of 10~280 rpm, among others. We invite you to review our catalog from HERE
We invite you to visit the products from our page Before making your purchase, you will be advised by our experts to make your experience excellent.