Why is the Radiant Baby Warmer effective?

It is a safe solution to preserve body temperature and avoid hypothermia. Most premature infants have a tendency to lose heat more quickly than full-term infants, making them particularly vulnerable to hypothermia. This condition can have serious consequences, particularly in newborns.
How do you prepare a radiant crib?

A radiant cradle is an electromedical equipment with wheels used to provide newborns with a comfortable thermal area that maintains their body temperature from 36 to 37 degrees. The thermal environment of this equipment can be controlled manually or by a servocontrol mechanism.
Children’s radiant heater: When should it be used?

A radiant infant heater is a medical equipment used in the field of neonatology and pediatrics, specifically in neonatal intensive care units, to provide newborns with a comfortable thermal area that maintains their body temperature from 36 to 37 degrees.
What are the different types of children’s heaters?
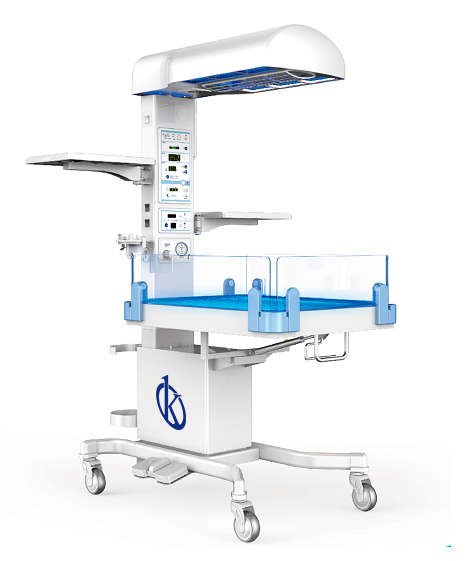
Childhood heaters are medical equipment designed to provide constant heat to low-weight newborns who have thermoregulation problems or who need constant interventions by medical staff, as their purpose is to maintain a temperature-controlled environment to help newborns maintain their body temperature…
What are the care and maintenance needs of a child radiant heater?
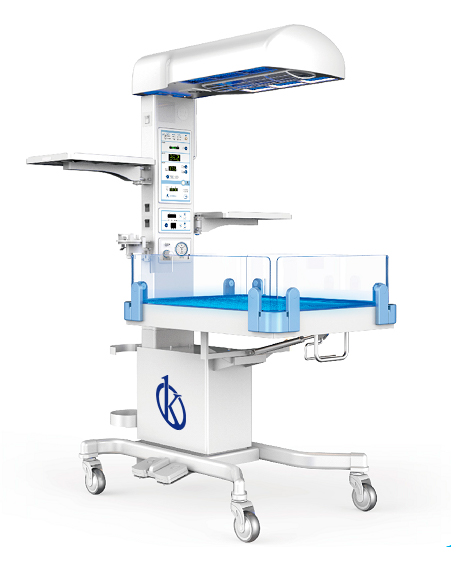
A radiant infant heater is a medical equipment commonly used in pediatrics and neonatology services, specifically in neonatal intensive care units, to provide newborns with a comfortable thermal area that maintains their body temperature from 36 to 37 degrees. This equipment works through a servo control…
Is a child radiant heater important?

A child radiant heater is a unit used to provide radiant heat to newborns in a comfortable thermal area that maintains their body temperature from 36 to 37 degrees. Newborns who are placed in radiant heaters are usually premature or low birth weight patients who have thermo-regulation problems and are therefore
When should Wheelchairs be used?

The wheelchair is a specialized equipment that helps in the movement for people who suffer from some kind of illness or injury that make it impossible and difficult to move. Depending on the type of condition that the user has, the wheelchair can be a technical aid that allows one to carry out daily activities independently. Regardless of the situation of each person, the wheelchair is a comfortable and adaptable device….
The Use of Wheelchairs for Rehabilitation
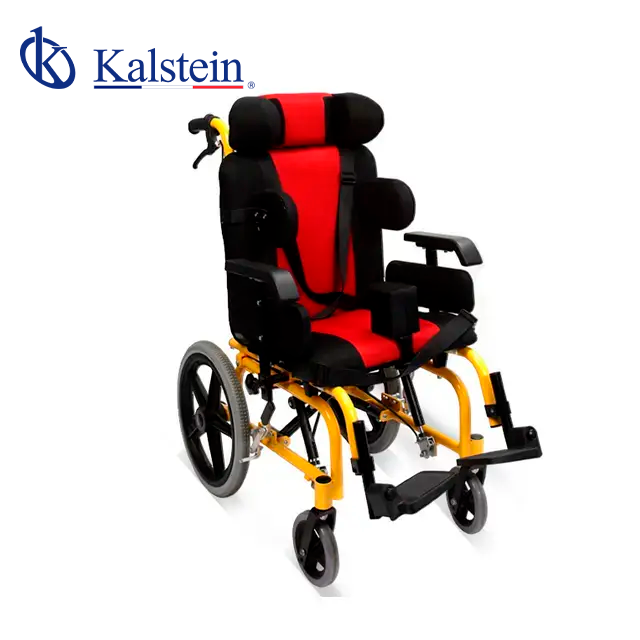

Patients in need of rehabilitation include those who have had injury due to trauma, stroke, birth defects or congenital disorders, serious infections, and developmental disorders, among others. The goal of this measure is to make the patient regain his independence, however, the type of rehabilitation is different for each person, since it depends on what is their problem or whether their disability is continuous or temporary…
Characteristics of the wheelchair for the transfer of patients
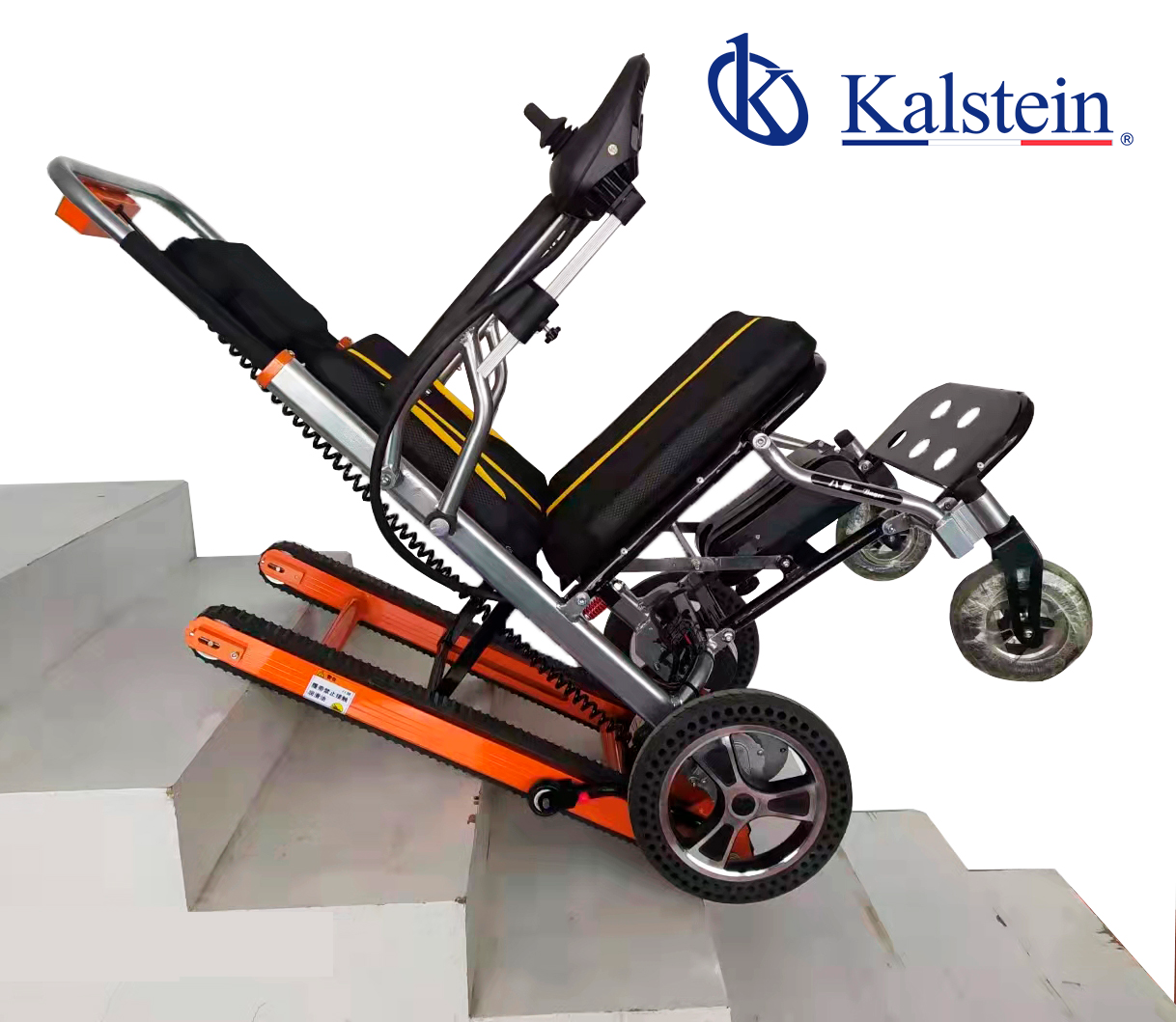

Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurological disease that causes atrophy in the brain and causes the death of brain neurons. Alzheimer’s, is a type of dementia that generates a continuous deterioration in the thought, behavior and social skills of a person. Symptoms due to this disease develop slowly and eventually worsen to the point that they are so severe that they interfere with a patient’s daily tasks.
The Rotary Evaporator in the Biology Laboratory
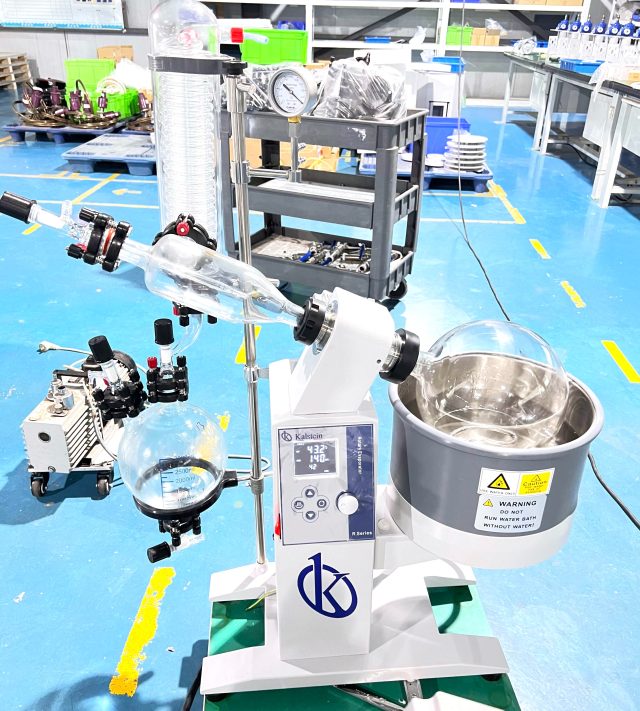

A rotary evaporator is laboratory equipment designed to facilitate the evaporation of liquids at high temperatures. It is an essential tool in the biology laboratory, where it is used to concentrate samples and perform other tasks related to research. The rotary evaporator consists of an evaporation tank, a heating unit, a condensing unit and a vacuum pump. All these elements are connected to each other by a series of pipes and hoses….
