Guaranteed Superior Quality: Overwhelming advantage of Kalstein Ice Maker in the laboratory field

The modern laboratory is always looking to improve its efficiency and ability to produce accurate and fast results. In this scenario, it is vital to have the best equipment available. One of these essential and often underestimated pieces of equipment is the ice maker. But, to which manufacturer should one turn to obtain the best performance and quality? The answer is Kalstein.
Safety Aspects When Using Underwater Treadmills for Pets: Tips and Recommendations

The growing world of veterinary rehabilitation has found in underwater treadmills a powerful tool for improving the health and well-being of pets. However, like any medical equipment, its use should be done with caution and knowledge. Kalstein, a renowned manufacturer of this type of equipment, prioritizes the safety of our pets and the peace of mind of their owners.
Kalstein and the Underwater Treadmill: An Innovation in the Treatment of Neurological Diseases in Pets

Neurological diseases in pets can be particularly challenging to treat. The novel introduction of the underwater treadmill onto the market, courtesy of Kalstein, a leading manufacturer of veterinary medical equipment, has revolutionized this type of treatment. This innovation offers an opportunity to improve our pets’ quality of life, at a cost that has revolutionized the relationship between prices, buying, and selling in the world of veterinary medicine.
Unlock New Scientific Possibilities with Kalstein’s Advanced Laboratory Incubators

The advancement of scientific research depends on the quality of the available laboratory equipment. Perhaps one of the most versatile and essential are the laboratory incubators. But, what makes a laboratory incubator special and why should you buy one from Kalstein? We’ll delve deeply into the superiority of these machines and how they could be the catalyst to take your scientific research to new heights.
The Role of Underwater Treadmills in Managing Chronic Pain in Pets

Based on recent data, the number of people adopting pets has soared exponentially over the last year. However, due to aging and various medical conditions, many pets suffer from chronic pain that affects their quality of life. A primary concern for pet owners is to ensure the comfort and well-being of their pets, with pain management being a critical aspect that must not be underestimated.
Maximize the Performance of Your Laboratory with the Compact Recirculating Chiller for Rotary Evaporators
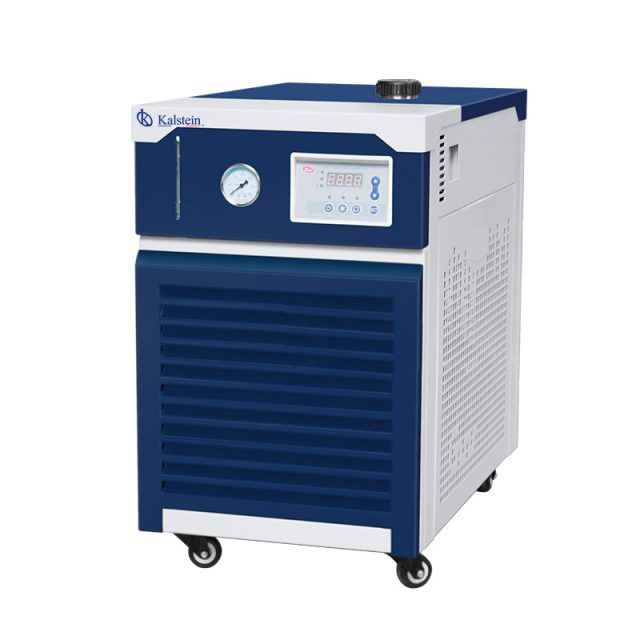

In the competitive world of laboratory science, efficiency is essential. The ability to perform tests and experiments quickly and accurately can be the difference between success and failure in scientific research. This is where Kalstein’s Compact Recirculating Chiller for Rotary Evaporators comes in as an indispensable tool. As a leading manufacturer in the market, Kalstein offers top-quality laboratory equipment to enhance efficiency and maximize productivity.
Swimming Pool vs Underwater Treadmill: What is Better for Your Pet’s Hydrotherapy?

Hydrotherapy for pets is becoming increasingly popular in the world of veterinary medicine and has become an exceptional option for rehabilitating our pets. Fortunately, companies like Kalstein, a leading manufacturer of veterinary medical equipment, offer a wide range of products for this purpose. But as a pet owner, the question may arise: Is a swimming pool or an underwater treadmill better for your pet’s hydrotherapy? In this article, we will examine both options, the prices, and where it is possible to buy and sell them.
Boosting Science with Electrophoresis Laboratory Equipment

Today, the importance of electrophoresis cannot be underestimated when talking about advancements in scientific research. As a leading manufacturer in the industry, Kalstein presents a range of high-quality electrophoresis equipment that is fundamental to various scientific sectors, from molecular biology to biochemistry and forensic medicine.
Improve the Quality of Your Scientific Work with the Best Homogenizers: The Advantages of Kalstein

In the world of science and research, homogenization is a critical process. This is where homogenizers come into play, a vital piece of equipment that contributes to the effectiveness of many experiments. But what exactly is a homogenizer? It is a tool developed to transform a sample from a heterogeneous state to a homogeneous state. This is achieved through the reduction in the size of particles and dispersion, ensuring a uniform mix.
Improving Color Measurement Accuracy with an Advanced Colorimeter: Elevating Your Laboratory to New Levels of Precision
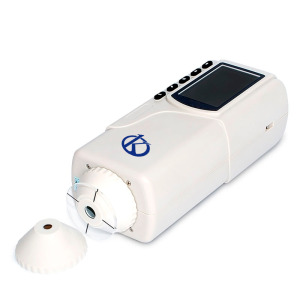
An advanced colorimeter is an essential scientific tool for its superior accuracy and its ability to analyze color with the most precise measurements possible. This revolutionary instrument captures light reflected from a sample and compares it with a preset standard, allowing for precise and uniform measurement of color hue and intensity.
